Flooded Tunnel Repair
Flooded Tunnel Repair
Underground Injection Grouting

A Spotlight on SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam and SealBoss EZ Flow Plastic Button Head Injection Packers
Introduction
Flooded Tunnel Repair: How to Stop Water Migration, Infiltration and Inflow in Underground Passages
Flooded tunnel repair is an essential process for maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of critical infrastructure like utility tunnels, storm drain systems, and primary sewer lines. These systems, when compromised by cracks, leaks, or structural weaknesses, are at risk of water migration and infiltration—a phenomenon known as Infiltration/Inflow (I/I) in the sanitary sewer industry. If left unchecked, water ingress not only deteriorates infrastructure but also poses significant environmental and safety risks.
With advanced tools, proven products, and effective repair methods, underground tunnel structures and expansive pipe systems can be restored to their intended performance. This article explores innovative techniques for flooded tunnel repair, with a focus on SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam and SealBoss EZ Flow Plastic Button Head Injection Packers.
The Challenge of Flooded Tunnel Repair
Journey Beneath: Unveiling the Underground
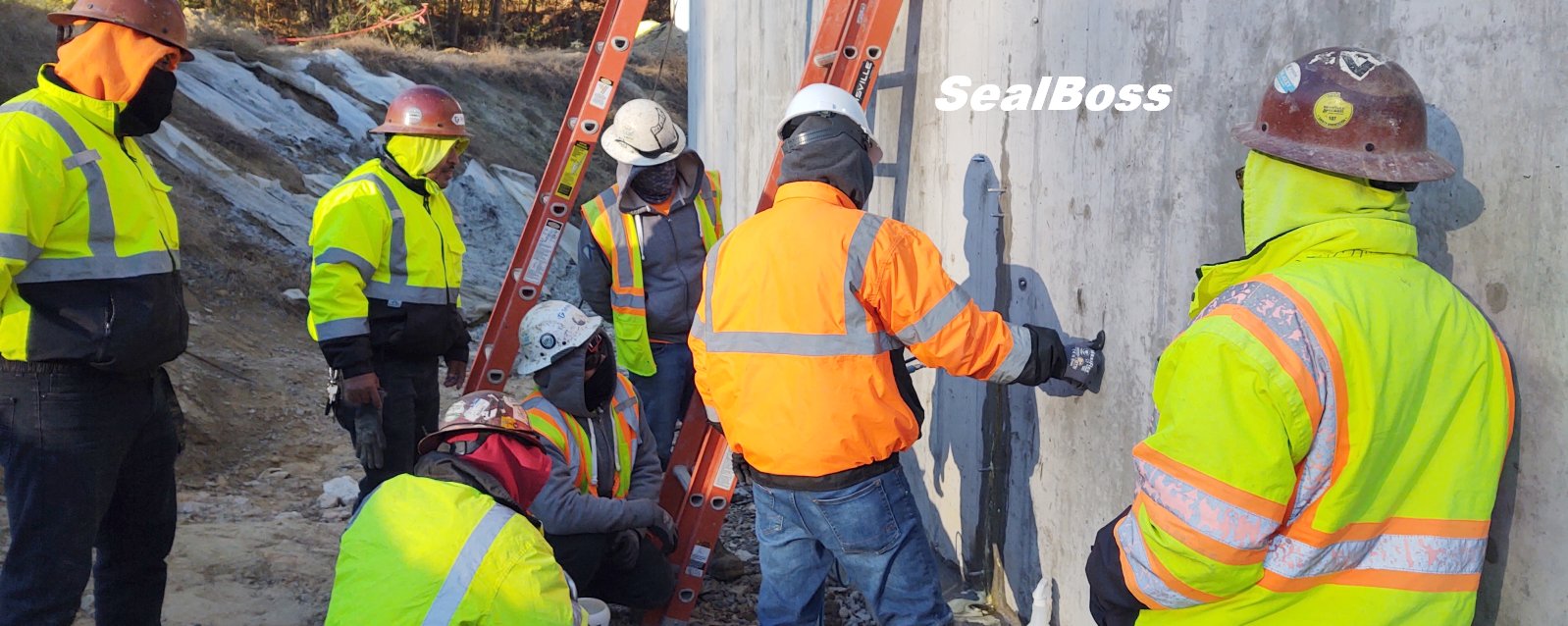
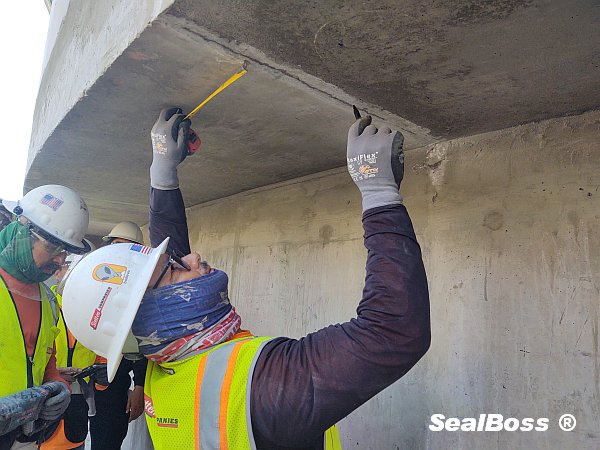
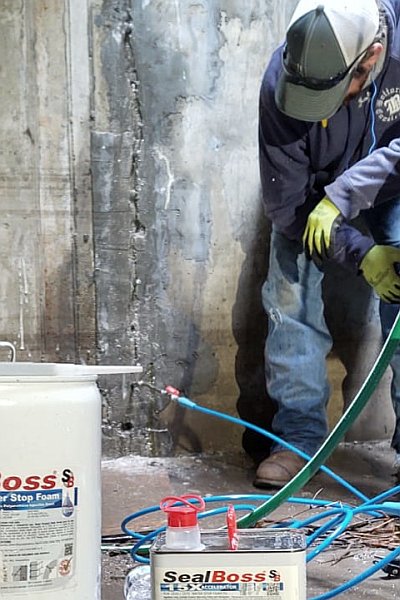
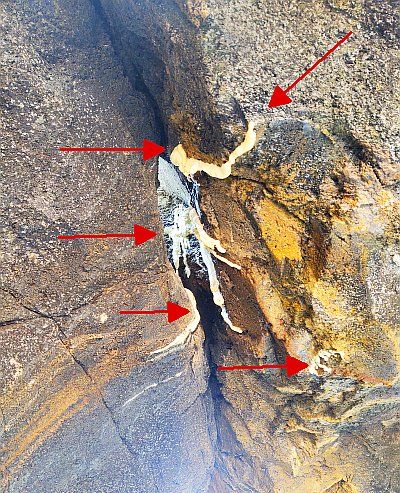
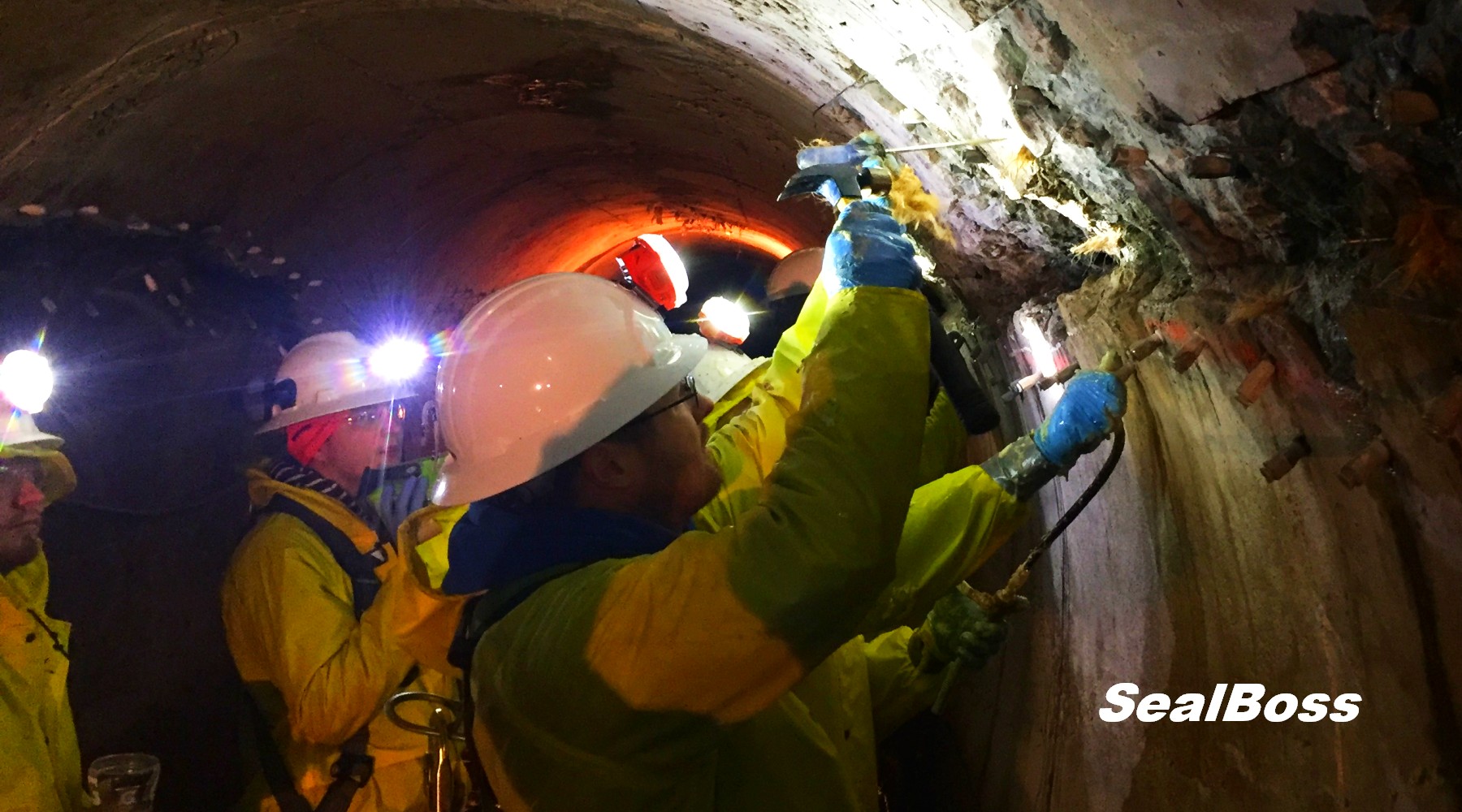
In this captivating video clip, viewers delve deep into a shadowy underground drainage tunnel, witnessing the significant impact of water ingress. Illuminated only by the beams of headlamps and makeshift lighting, the scene reveals a structure submerged in over a foot of water.
Despite the uninviting environment and jobsite conditions, the skilled injection team remains focused and determined, united by one mission: to repair and seal the structure.
Enter the SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam and SealBoss EZ Flow Plastic Button Head Injection Packers – a dynamic duo that promises effective and lasting solutions.
SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam: A Game-Changer in Flooded Tunnel Repair
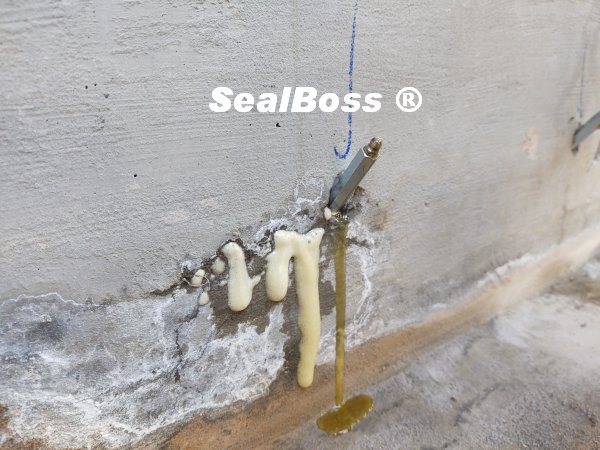
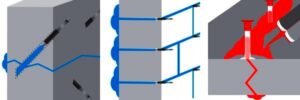
The SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam is a polyurethane-based chemical grout renowned for its ability to stop water migration efficiently.
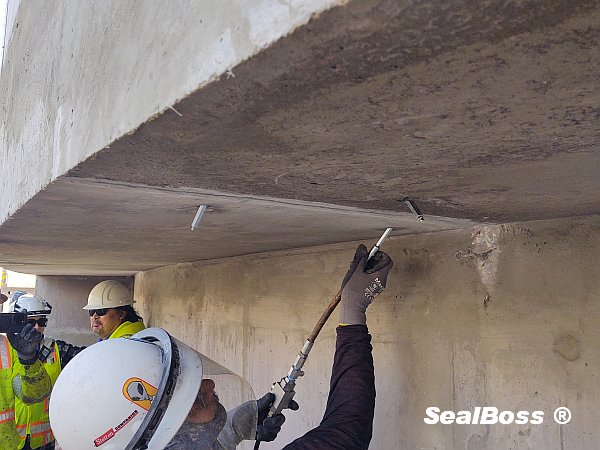
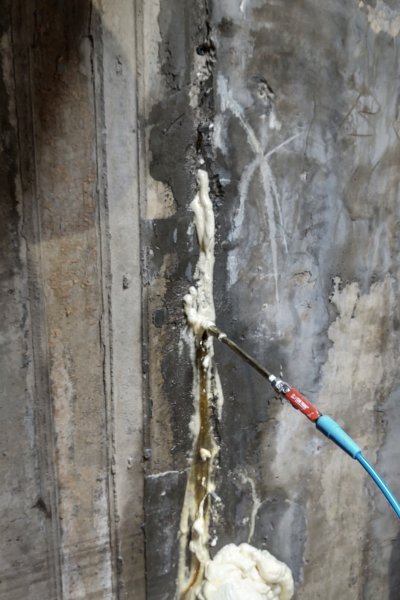
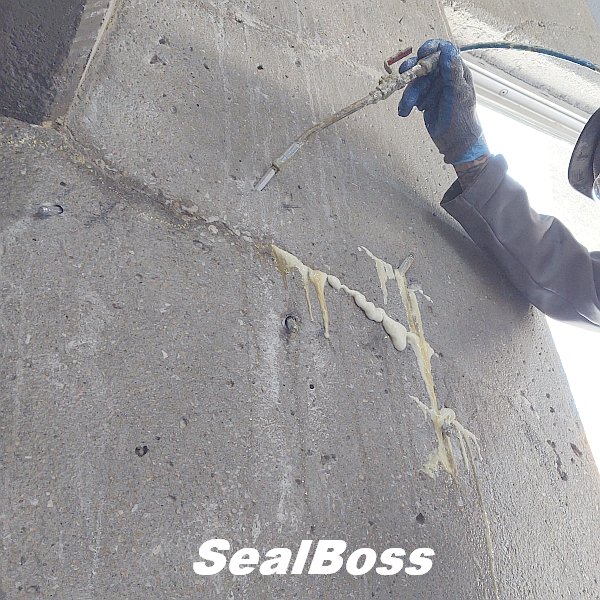
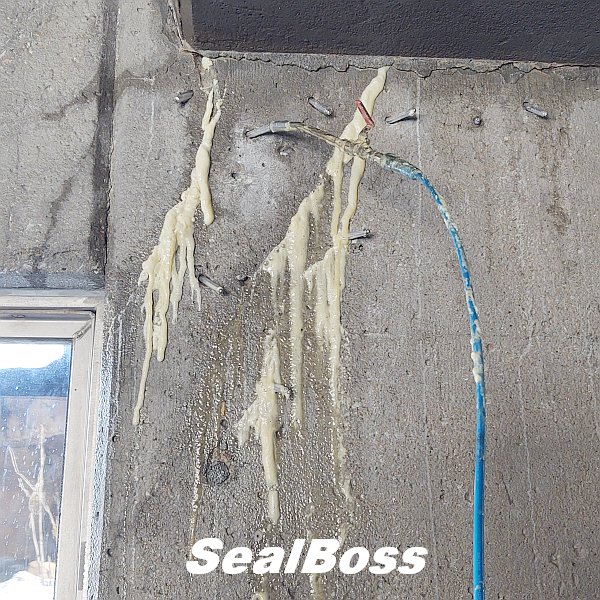
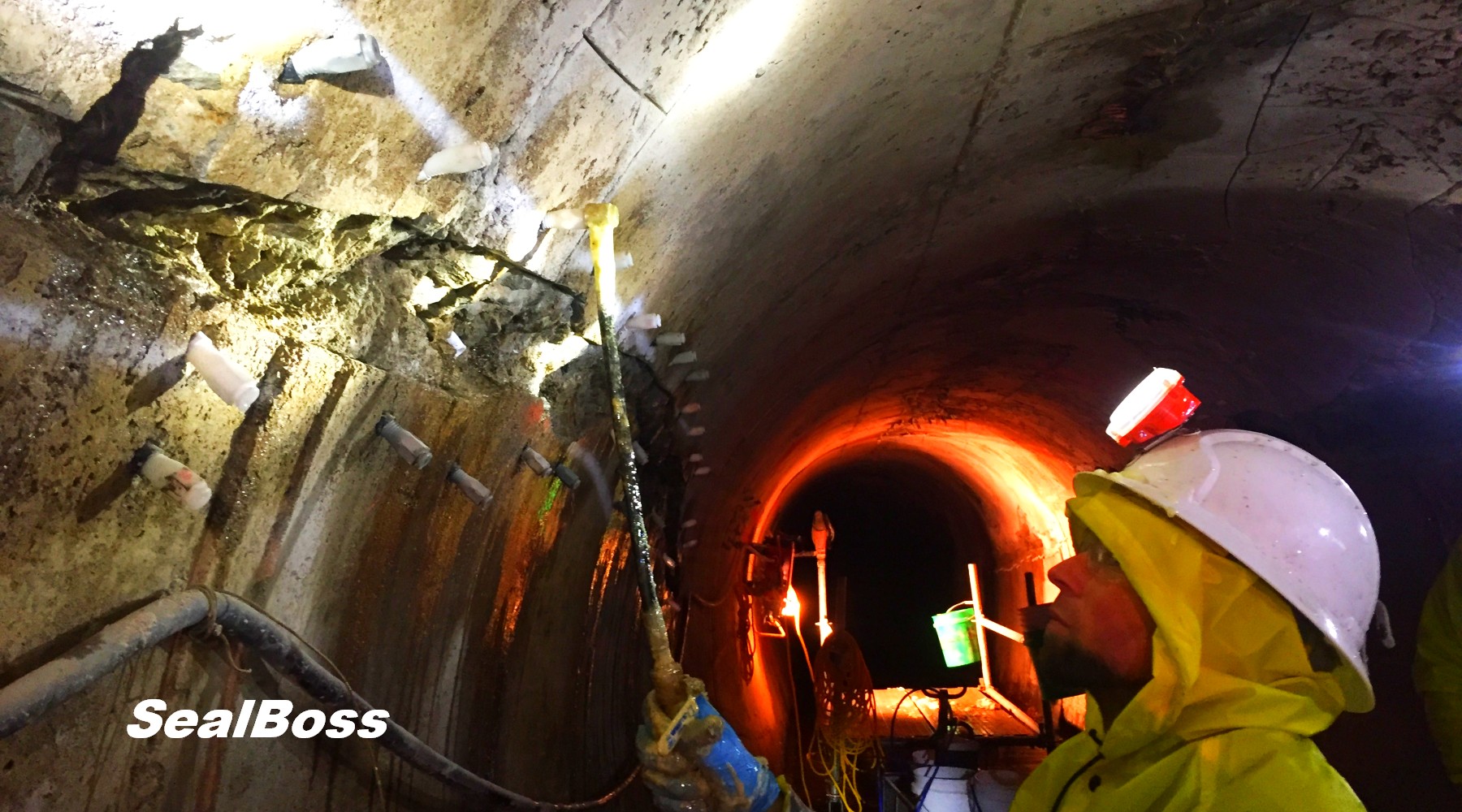
This injection project showcases the power of SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam. As the foam is injected, it migrates rapidly, filling cracks, fissures and voids, effectively stopping water ingress. The foam’s expansion and curing properties make it an ideal solution for such challenging environments, ensuring that the tunnel’s water tight integrity is restored.
Key Benefits:
High Expansion Rate: The foam effectively seals even the smallest gaps, preventing water flow.
Fast Curing Time: Once injected, it hardens quickly to form a durable barrier against water.
Versatility: Suitable for use in a variety of underground environments, including tunnels, pipelines, and many underground commercial and residential structures.
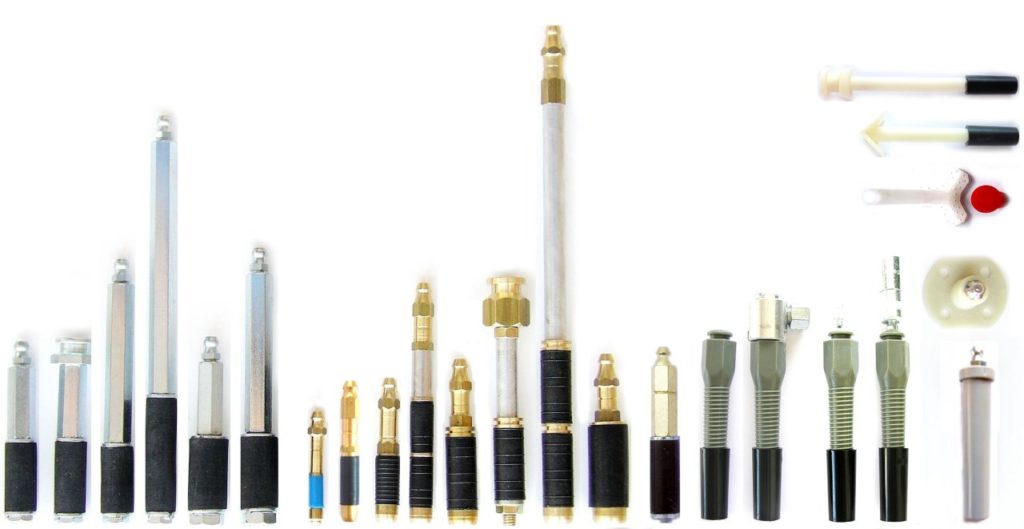
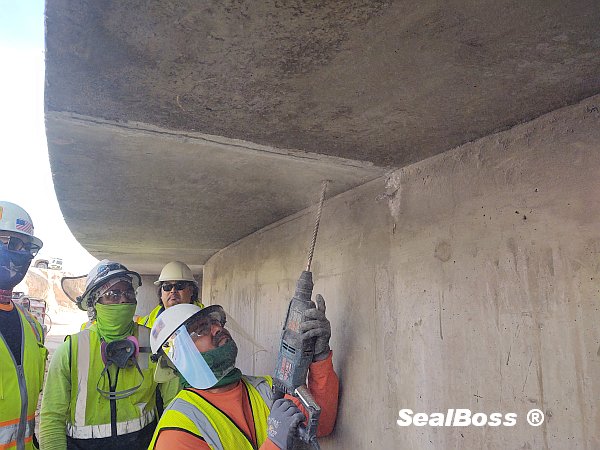
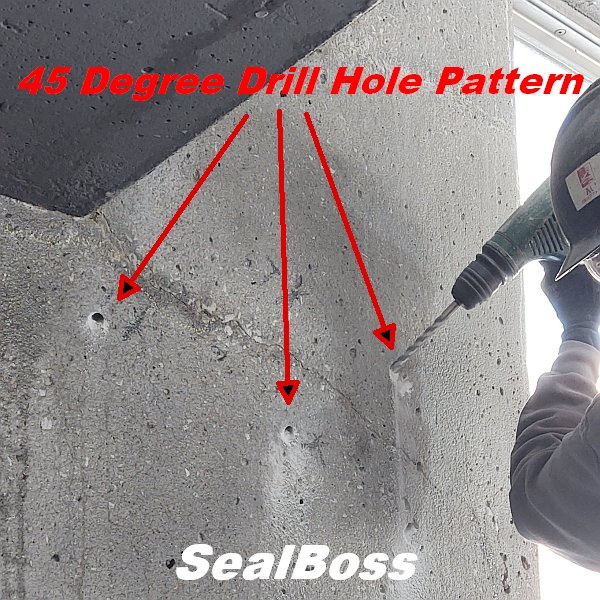
The Role of SealBoss EZ Flow Plastic Button Head Injection Packers for Floded Tunnel Repair
Ensuring Secure and Highly Efficient Grout Delivery
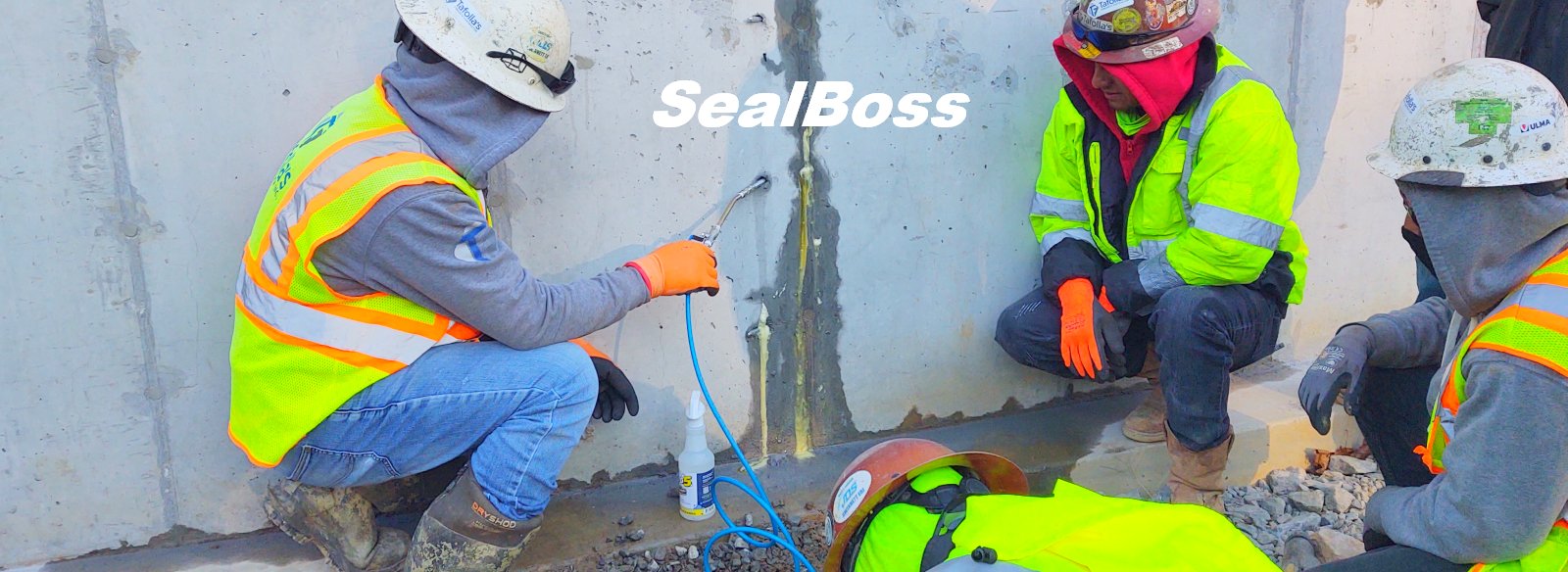
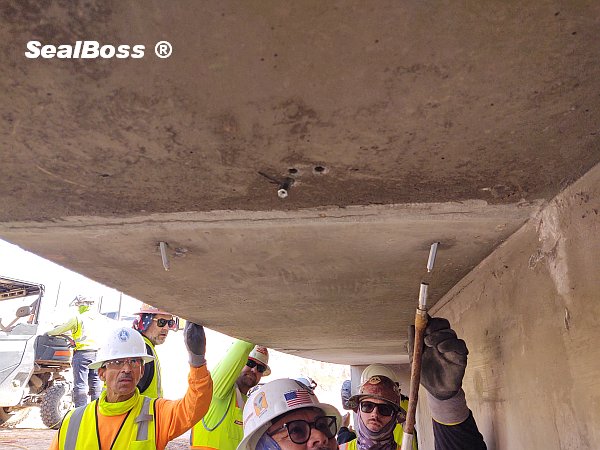
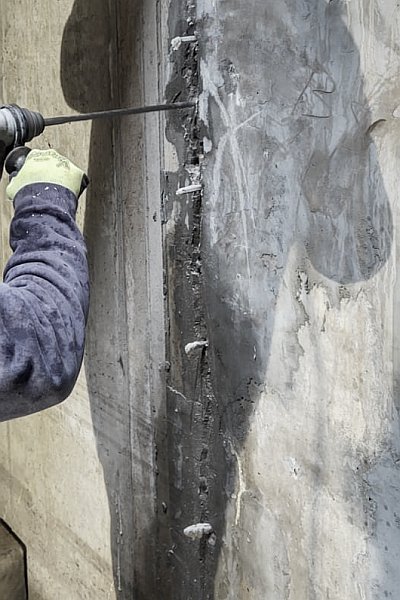
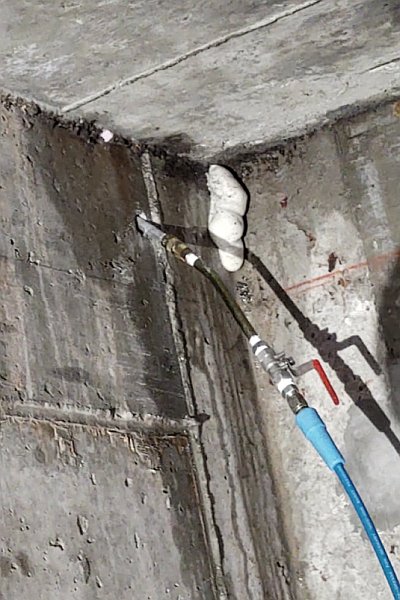
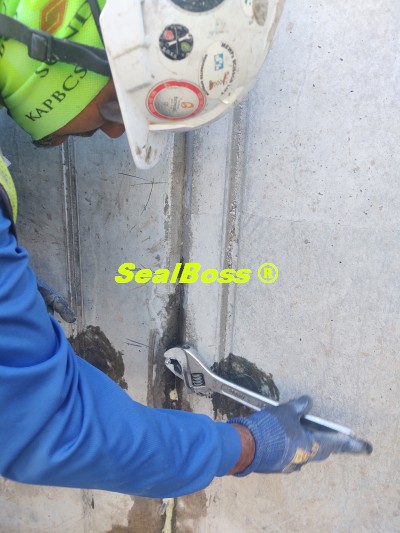
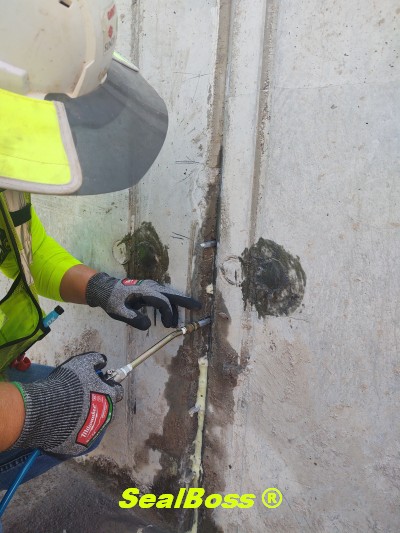
The effectiveness of SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam depends on precise delivery, which is made possible by SealBoss EZ Flow Plastic Button Head Injection Packers. These innovative injection tools are designed for efficiency, reliability, and ease of use in demanding conditions.
One of the highlights of this injection project is the impeccable, leak-free connection between the injection grout line’s slide coupler and the button head packers that have been installed. This is largely attributed to the purpose driven design of the button head packer and slide coupler, ensuring a secure connection, and eliminating the need for the contractor to manually hold it in place.
Additionally, the expansive inner diameter of both the coupler and button head, combined with the oversized ball valve design, facilitates the pumping and delivery of chemical grout at impressive flow rates and volumes. This guarantees that the foam is dispensed exactly where required.
SealBoss EZ Flow Plastic Button Head Injection Packers are instrumental in efficiently and securely delivering the SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam. They ensure the foam is dispensed at high volumes and appropriate pressures, streamlining and enhancing the repair process.

Conclusion
With the right tools and products in place, underground injection and flooded tunnel repair no longer needs to be a daunting task for crack injection teams. With the combined power of SealBoss 1510 Water Stop Foam and SealBoss EZ Flow Plastic Button Head Injection Packers, even challenging grout injection environments can be tackled with confidence.
This project serves as a powerful example of how cutting-edge materials and innovative tools can effectively restore the integrity of underground infrastructure, such as tunnels and pipelines. As the industry continues to evolve, solutions like these will remain at the forefront, enabling contractors to tackle water migration and infiltration with precision and reliability.
Investing in quality products and adopting proven repair techniques ensures not only the longevity of critical infrastructure but also the safety and well-being of communities that depend on it.
Related Articles
Leak-Seal Foam Grout
Water Stop Foam Grout
Hydrophobic Injection Foam Grout
Our #1 Selling Polyurethane Injection Foam
Water Cut-Off Injection Grout
Unregulated for transport. Drinking Water Contact meets NSF/ANSI 61 Section 5 requirements. 1510 PU Foam & Oakum Pipe Plug Kit
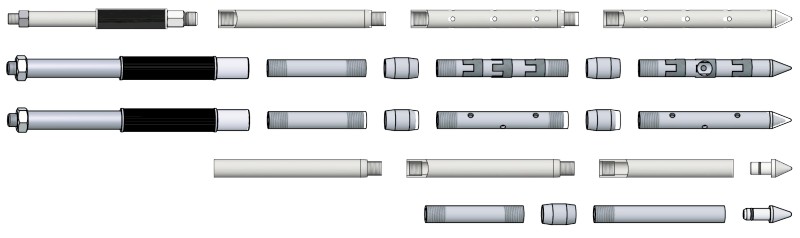
EZ FLOW PLASTIC INJECTION PACKER | PLASTIC PORT
High Volume Easy Flow Packer | EZ Flow Packer Design
Plastic packer with large inner diameter for high volume product flow. The packer is threaded and equipped with a removable, sleeve for good grip. Free-floating large ball valve for high volume applications. Buttonhead top for secure connection and minimal leakage. Suitable for PU grouts, Acrylate Gels (Acrylic Gels). Also available with zerk fitting.