Thermography - Chemical Injection Grouting
Infrared Thermography: Fast and Reliable Assessment of Chemically Grouted Shotcrete Structures
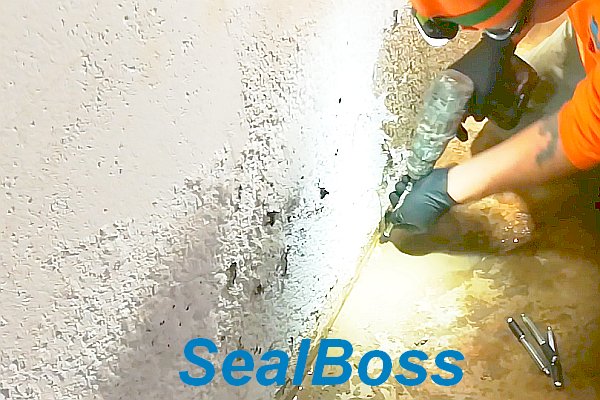
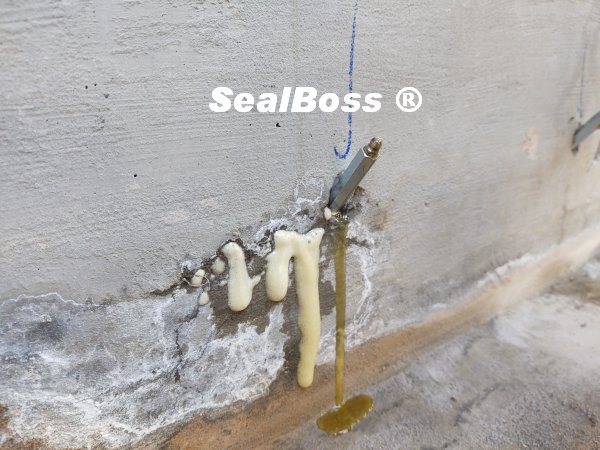
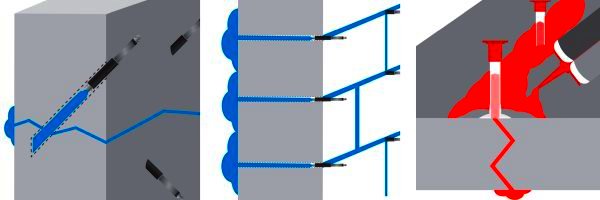
Chemical grout injection is a common method for concrete crack and water infiltration repair of concrete structures. During the process, a chemical mixture is injected into the ground or structure, resulting in an exothermic reaction that releases heat. This heat can be detected using thermographic imaging equipment, which can discern the relative differences between thermal masses or thermal capacities in grouted and ungrouted areas of the structure.
Non-Destructive and Non-Invasive Testing
Infrared thermography is an effective tool for providing a color picture that indicates the differences in energy or heat emitted from the surface of a structure. This image can assist in providing a quality assessment of the grout injection procedure, including the penetration, travel, and effectiveness of the grout. Additionally, thermographic imaging can also be used to monitor the curing process of the grout and detect any potential defects or anomalies.
Thermography | Measuring Effectiveness of Chemical Injection Grouting
Thermographic imaging has become an essential tool for many industries, including construction and engineering, as it provides a non-invasive and non-destructive method for evaluating the condition of structures. With the ability to detect heat and energy emitted from a structure, thermographic imaging can identify areas of concern and help prevent potential failures.
SealBoss, with over three decades of experience in the concrete repair industry, has made significant strides in developing materials and procedures for achieving effective and long-lasting chemical grout placement.
Despite this progress, confirming proper grouting through non-destructive means has remained a challenge for quality assurance purposes. The adoption of infrared thermography (IR) as a monitoring tool can aid in detecting and measuring product permeation and travel in grouted concrete and shotcrete structures for quality assurance.
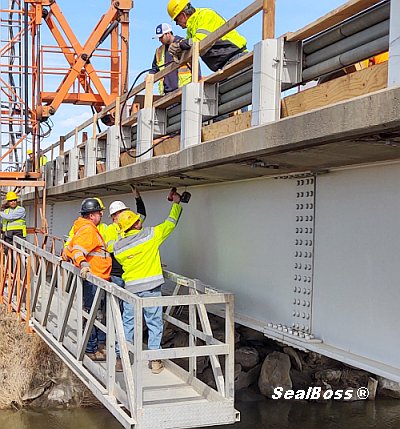
Thermal Imaging | Shotcrete Grout Injection
Shotcrete is gaining popularity in below-grade construction. The trend of using shotcrete in lieu of traditional cast-in-place (CIP) concrete can be accredited to lower overall construction cost and time saved by not having to install formwork.
However, the use of shotcrete can result in a less than solid structure and may exhibit segregation, honeycombing, voids and air pockets which consequently leads to a higher incidence of water ingress in below-grade structures.
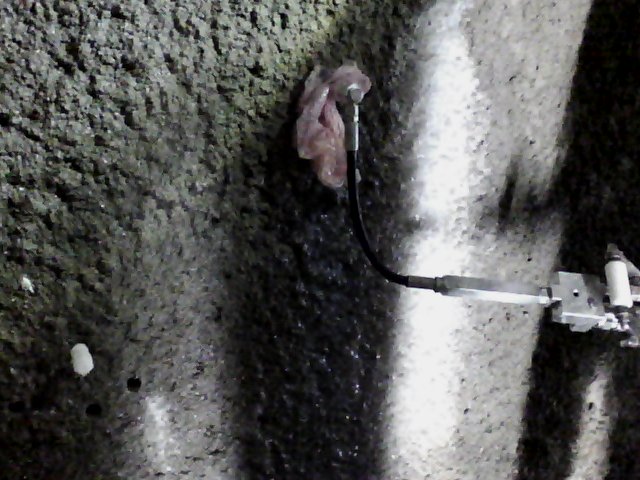

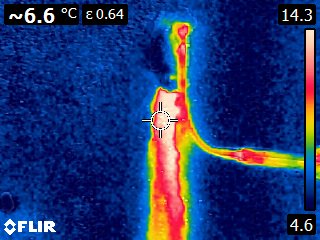
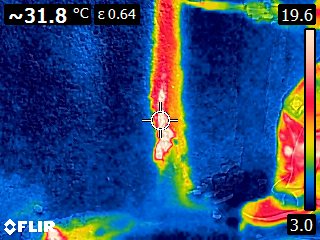
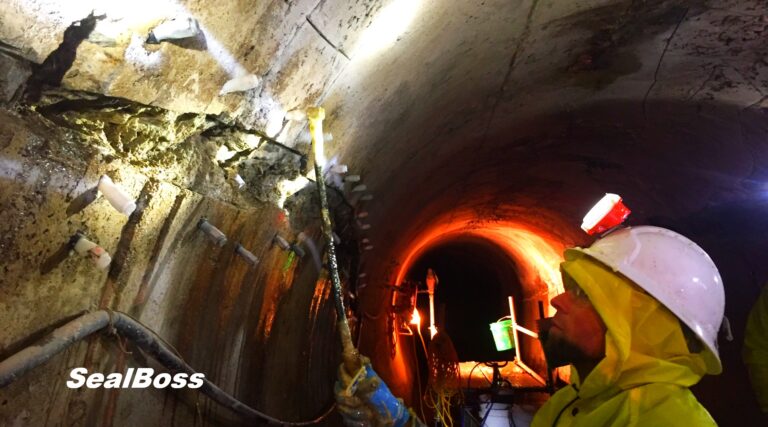
Thermographic Images: Shotcrete Tunnel Injection with SealBoss 2400 Acrylate Gel
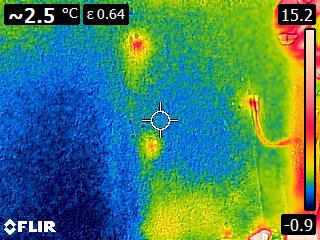

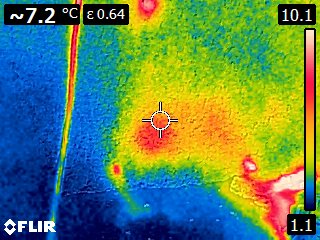
As the gel undergoes its exothermic reaction and spreads through pressure injection, it generates heat that is transferred to the surrounding substrate. The resulting increase in temperature can be detected and visualized through color graded infrared (IR) pictures and videos.
Thermal images captured by the camera demonstrate the injection gel penetrating the structure and gradually expanding, warming the shotcrete in the process.
Synopsis – Chemical Grouting Thermography
During the exothermic reaction of chemical grout injected into the structure, energy is given off in the form of heat.
This heat can be detected by thermographic imaging equipment. Infrared thermography is able to discern the relative differences between thermal mass or thermal capacity in grouted and ungrouted areas of the structure and provide a color picture indicating differences in energy / heat emitted from the surface of structure.
The interpretation of the image can assist in providing a quality assessment regarding the penetration, travel and effectiveness of the grout injection procedure.